Would you like to learn how to do a GLPI installation on Ubuntu Linux? In this tutorial, we are going to show you how to install, configure and access the GLPI on a computer running Ubuntu Linux version 17.
Hardware List:
The following section presents the list of equipment used to create this GLPI tutorial.
Every piece of hardware listed above can be found at Amazon website.
GLPI Related Tutorial:
On this page, we offer quick access to a list of tutorials related to GLPI installation.
Tutorial - NTP on Ubuntu Linux
First, we are going to configure the system to use the correct date and time using NTP.
On the Linux console, use the following commands to set the correct timezone.
# dpkg-reconfigure tzdata
Install the Ntpdate package and set the correct date and time immediately.
# apt-get update
# apt-get install ntpdate
# ntpdate pool.ntp.br
The Ntpdate command was used to set the correct date and time using the server: pool.ntp.br
Let's install the NTP service.
# apt-get install ntp
NTP is the service that will keep our server updated.
Use the command date to check the date and time configured on your Ubuntu Linux.
# date
If the system shown the correct date and time, this means that you followed all the steps correctly.
Tutorial - MariaDB on Ubuntu Linux
Now, we can proceed to the installation of the database service.
On the Linux console, use the following commands to install the required packages.
# apt-get update
# apt-get install software-properties-common
# apt-key adv --recv-keys --keyserver hkp://keyserver.ubuntu.com:80 0xF1656F24C74CD1D8
# add-apt-repository 'deb [arch=amd64,i386] http://nyc2.mirrors.digitalocean.com/mariadb/repo/10.2/ubuntu artful main'
# apt-get update
# apt-get install mariadb-server mariadb-client
The installation wizard will ask you for a password to the root user.
After finishing the installation, use the following command to access the MariaDB database server.
To access the database server, enter the password set on the MariaDB server installation wizard.
# mysql -u root -p
Use the following SQL command to create a database named glpi.
CREATE DATABASE glpi CHARACTER SET UTF8 COLLATE UTF8_BIN;
Use the following SQL command to create a database user named glpi.
CREATE USER 'glpi'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'kamisama123';
Give the sql user named glpi permission over the database named glpi.
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON glpi.* TO 'glpi'@'%';
quit;
Tutorial - Installing Apache on Linux
Now, we need to install the Apache web server and all the required software.
On the Linux console, use the following commands to install the required packages.
# apt-get install apache2 php libapache2-mod-php
# apt-get install php-json php-gd php-curl php-mysql php-mbstring php-cas
# apt-get install php-xml php-cli php-imap php-ldap php-xmlrpc php-apcu
Now, you should find the location of the php.ini file on your system.
After finding, you need to edit the php.ini file.
# updatedb
# locate php.ini
# vi /etc/php/7.0/apache2/php.ini
Keep in mind that your PHP version and the location of the file may not be the same of mine.
Here is the original file, before our configuration.
file_uploads = On
max_execution_time = 30
memory_limit = 128M
post_max_size = 8M
max_input_time = 60
; max_input_vars = 1000
Here is the new file with our configuration.
file_uploads = On
max_execution_time = 300
memory_limit = 256M
post_max_size = 32M
max_input_time = 60
max_input_vars = 4440
You should also restart apache manually and verify the service status.
# service apache2 stop
# service apache2 start
# service apache2 status
Here is an example of the APache service status output.
● apache2.service - LSB: Apache2 web server
Loaded: loaded (/etc/init.d/apache2; bad; vendor preset: enabled)
Drop-In: /lib/systemd/system/apache2.service.d
└─apache2-systemd.conf
Active: active (running) since Mon 2018-04-23 00:02:09 -03; 1min 4s ago
Tutorial - GLPI Installation on Ubuntu
Now, we need to install the GLPI Ubuntu Linux.
On the Linux console, use the following commands to download the GLPI package.
# mkdir /downloads
# cd /downloads
# wget https://github.com/glpi-project/glpi/releases/download/9.2.2/glpi-9.2.2.tgz
# tar -zxvf glpi-9.2.2.tgz
# ls
glpi glpi-9.2.2.tgz
Move all the GLPI files to the root directory of your Apache installation.
Set the correct file permission on all moved files.
# mkdir /var/www/html/glpi
# mv glpi/* /var/www/html/glpi
# chown www-data.www-data /var/www/html/glpi/* -R
Create an Apache configuration file named glpi.conf.
# vi /etc/apache2/conf-available/glpi.conf
Here is the new file configuration.
<Directory /var/www/html/glpi>
AllowOverride All
</Directory>
<Directory /var/www/html/glpi/config>
Options -Indexes
</Directory>
<Directory /var/www/html/glpi/files>
Options -Indexes
</Directory>
Enable the new configuration on Apache.
# a2enconf glpi
Restart the Apache service.
# service apache2 stop
# service apache2 start
Open your browser and enter the IP address of your web server plus /glpi.
In our example, the following URL was entered in the Browser:
• http://35.162.85.57/glpi
The GLPI web installation interface should be presented.
Select the desired language.
On the next screen, you will have to accept the GLPI license.
On the next screen, you will have to click on the Install button.
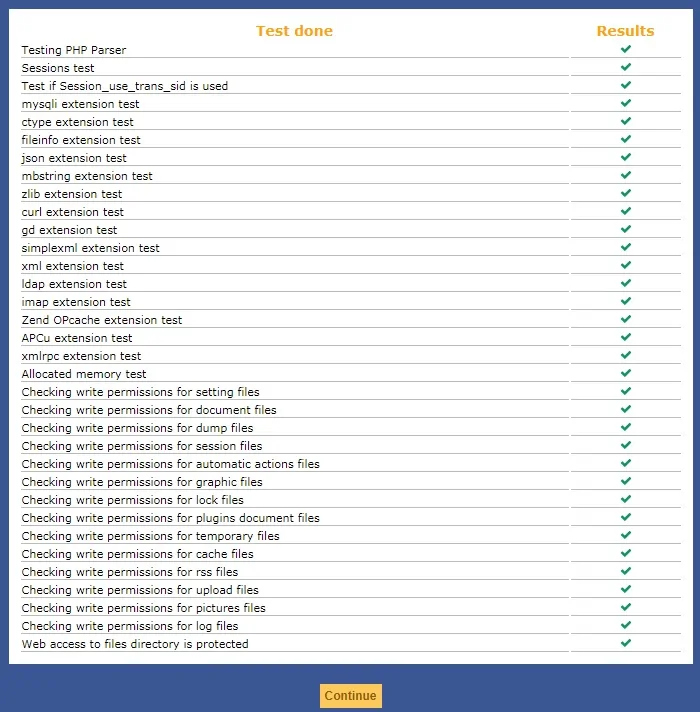
On the next screen, you will have to click on the Install button.
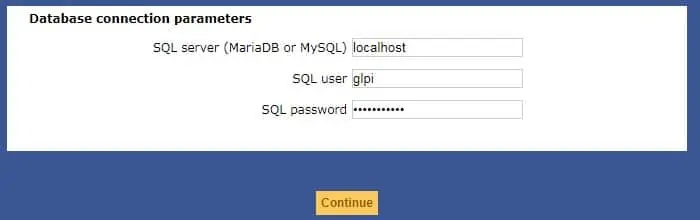
On the next screen, you will have to enter the Database information required to connect to the GLPI database.
• Host: localhost
• Database Username: glpi
• Database Password: *****
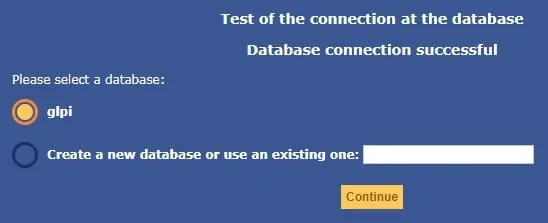
On the next screen, you will have to select the GLPI database and click on the Continue button.
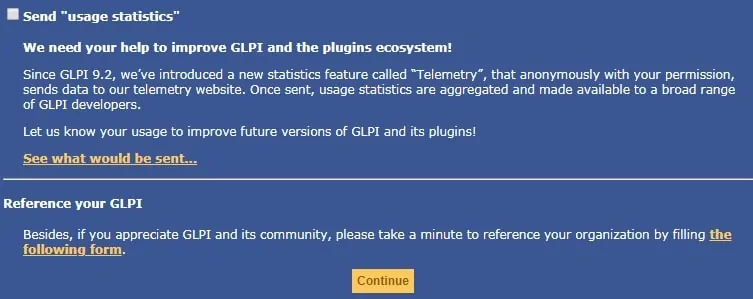
On the next screen, you will have to uncheck the checkbox an click on the Continue button.
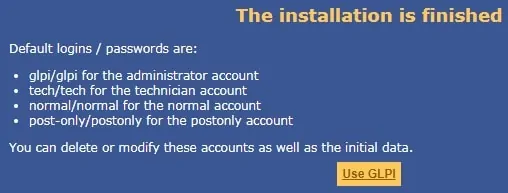
On the next screen, you will be presented with the default logins and passwords of GLPI.
Finally, you will be resented with the GLPI login screen.
After a successful login, you will be sent to the GLPI Dashboard.
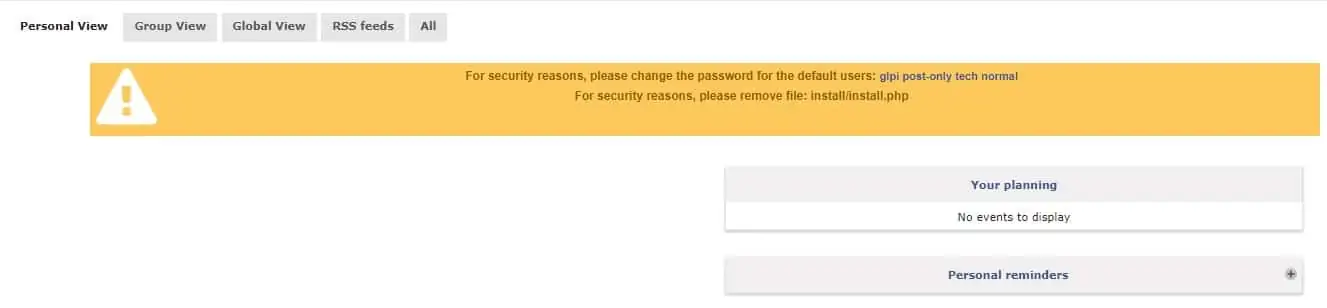
On the Linux console, delete the install.php file.
# rm /var/www/html/glpi/install/install.php
Congratulations, you have installed the GLPI system on Ubuntu Linux.
