Would you like to learn how to set up the Radius authentication of the Kubernetes Dashboard with Freeradius? In this tutorial, we are going to show you how to authenticate Kubernetes Dashboard users using the Radius protocol and the Freeradius service on a computer running Ubuntu Linux.
• Ubuntu 20
• Ubuntu 19
• Ubuntu 18
• Kubernetes 1.18
This tutorial will install a single-node Kubernetes cluster.
In our example, the IP address of the Kubernetes master node is 192.168.15.200.
In our example, the IP address of the Radius server is 192.168.15.10.
Kubernetes - Tutorials
On this page, we offer quick access to a list of tutorials related to Kubernetes.
Tutorial - FreeRadius Server Installation on Ubuntu Linux
• IP - 192.168.15.10
• Operacional System - Ubuntu 20
• Hostname - FREERADIUS
On the Linux console, use the following commands to install the FreeRadius service.
Now, we need to add FreeRadius clients to the clients.conf;.
Locate and edit the clients.conf.
Add the following lines at the end of the clients.conf file.
In our example, we are adding 1 client device:
The device was named KUBERNETES and has the IP address 192.168.15.200.
In our example, we set the secret: KAMISAMA123.
Now, we need to add FreeRadius users to the USERS configuration file.
Find and edit the Freeradius user configuration file.
Add the following lines at the end of the file
In our example, we create a user account named ADMIN.
Restart the Freeradius server.
Test your radius server configuration file.
You have finished the Freeradius installation on Ubuntu Linux.
Tutorial Kubernetes - Master node Installation
Install the list of required packages.
Install the Docker service.
Enable the Docker service during boot.
Edit the Docker service configuration file.
Add the following configuration at the end of the item named: EXECSTART
Here is the file before our configuration.
Here is the file after our configuration.
Create a System configuration file.
Here is the file content.
Enable the System configuration file.
Edit the configuration file named: MODULES.CONF
Add the following configuration at the end of this file.
Edit the FSTAB configuration file and disable the use of Swap memory.
Here is the file before our configuration.
Here is the file after our configuration.
Set a unique hostname.
Create a file to configure the required environment variables.
Here is the file content.
Reboot the computer.
Download and install the Kubernetes repository key.
Add the official Kubernetes repository.
Install the Kubernetes packages.
Download the required Kubernetes images.
Here is the command output.
Initialize the Kubernetes cluster.
Here is the command output.
Take note of the command to add nodes to the Kubernetes cluster.
Set the correct file permission on the Kubernetes configuration file.
Install the required network configuration.
By default, the Kubernetes master node is not allowed to run PODS.
Optionally, enable the Kubernetes master node to run PODS.
In our example, we are using a single-node Kubernetes cluster.
Tutorial - Kubernetes Dashboard installation
Install the list of required packages.
Download the required YAML file.
Install the Kubernetes Dashboard.
Here is the command output.
Create a service account for the Dashboard.
Configure the Cluster admin role to the Dashboard service account.
Create a service account for the Apache proxy.
Configure the Cluster admin role to the Apache proxy account.
List the Apache secret available on the Kubernetes server.
Here is the command output.
Notice that your secret's name will not be the same as ours.
Get the value of the Apache secret token.
Here is the command output.
Take note of the Apache token value.
In our example, this is the token value:
List the Dashboard service cluster IP address.
Here is the command output.
Take note of the cluster IP address and TCP port.
In our example, the Dashboard cluster is using the TCP port 443 and the IP address 10.107.55.24.
You have finished the required Dashboard configuration.
Kubernetes Proxy - Radius authentication using Apache
On the Master node, install the Apache server.
Enable the required Apache modules.
Edit the Apache configuration file.
Add the following lines to the end of this file.
Create a private key and certificate using the OpenSSL command.
Enter the requested information.
In the option named COMMON_NAME, you must enter the IP address or the hostname.
In our example, we use the IP address: 192.168.15.200
Convert your existing Kubernetes proxy certificate and the key to a single file in the PEM format.
Edit the Apache configuration file for the default website.
Here is the file, before our configuration.
Here is the file, after our configuration.
Change the IP address of the configuration item named ADDRADIUSAUTH to the IP address of the Radius server.
Change the IP address of the configuration items named PROXYPASS and PROXYPASSREVERSE to the IP address of the Dashboard cluster.
Change the token value of the CI named REQUESTHEADER to the Apache secret token value created earlier.
In our example, we enabled the use of HTTPS using self-signed certificates.
In our example, we configured the use of RADIUS authentication.
Apache will represent HTTPS communication between the user and the Dashboard cluster IP address.
Apache will use a certificate and key created automatically during the Kubernetes server installation to perform mutual TLS authentication on the Dashboard.
The Apache server will add a header to all packets sent to the Dashboard.
This header is named AUTHORIZATION BEARER and contains the secret token created earlier in the Apache proxy.
Apache will also redirect HTTP users to the HTTPS version of the requested URL.
Restart the Apache service.
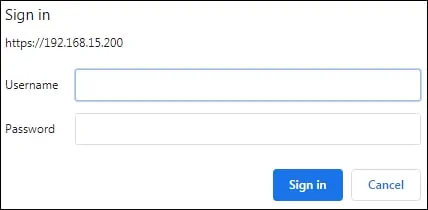
Open your browser and access the HTTPS version of the Apache server's IP address.
In our example, the following URL was entered in the browser:
• https://192.168.15.200
The Apache server will require you to perform user authentication.
After a successful login, the Kubernetes Dashboard should be presented.
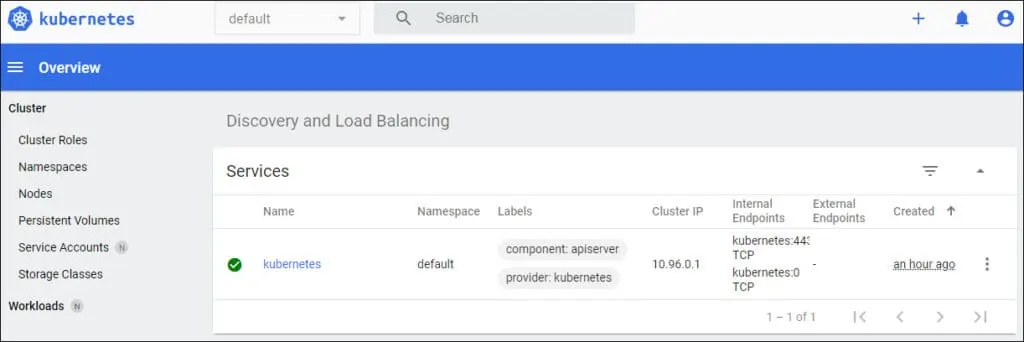
The Apache proxy will automatically authenticate to the Kubernetes Dashboard using the feature named: AUTH HEADER.
You have successfully completed the configuration of Apache as a proxy for the Kubernetes Dashboard.
