Would you like to learn how to use a group policy to configure the Powershell Constrained Mode on Windows? In this tutorial, we will show you how to create a group policy to enable the Powershell Constrained Mode.
• Windows 2012 R2
• Windows 2016
• Windows 2019
• Windows 2022
• Windows 10
• Windows 11
Equipment list
Here you can find the list of equipment used to create this tutorial.
This link will also show the software list used to create this tutorial.
Windows Related Tutorial:
On this page, we offer quick access to a list of tutorials related to Windows.
Tutorial GPO - Powershell Constrained Mode
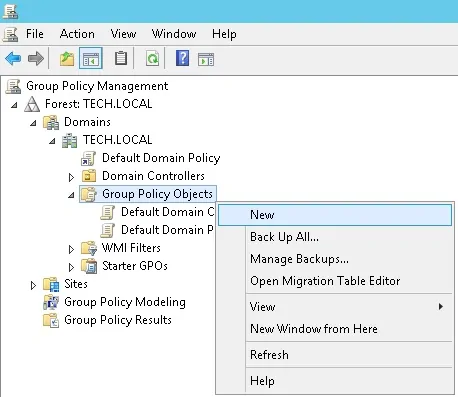
On the domain controller, open the group policy management tool.

Create a new group policy.
Enter a name for the new group policy.
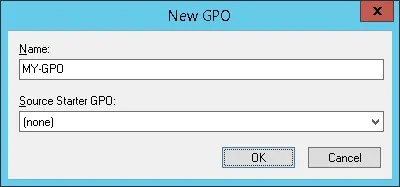
In our example, the new GPO was named: MY-GPO.
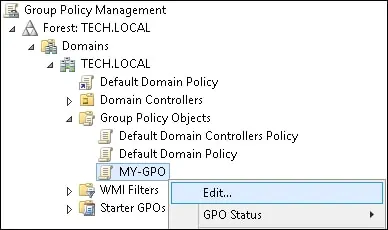
On the Group Policy Management screen, expand the folder named Group Policy Objects.
Right-click your new Group Policy Object and select the Edit option.
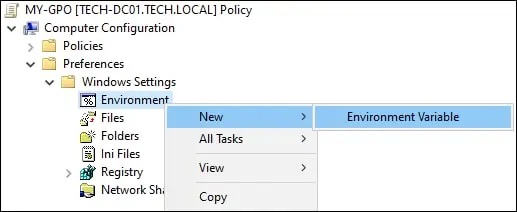
On the group policy editor screen, expand the Computer configuration folder and locate the following item.
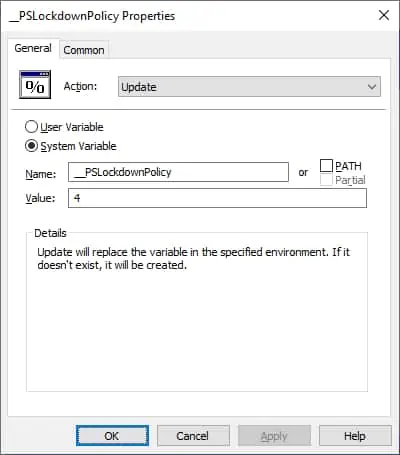
Create a new environment variable.
Perform the following configuration.
Click on the OK button.
To save the group policy configuration, you need to close the Group Policy editor.
Congratulations! You have finished the GPO creation.
Tutorial GPO - Powershell Constrained Mode
On the Group policy management screen, you need to right-click the Organizational Unit desired and select the option to link an existent GPO.
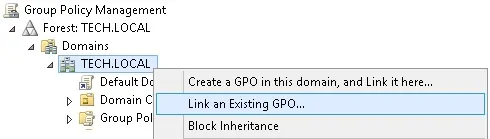
In our example, we are going to link the group policy named MY-GPO to the root of the domain.
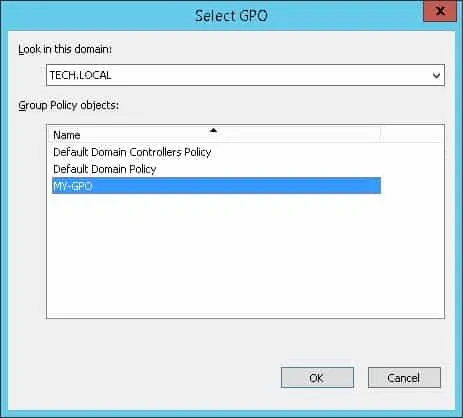
After applying the GPO you need to wait for 10 or 20 minutes.
During this time the GPO will be replicated to other domain controllers.
On a remote computer, start a Powershell command line.

Verify if the environment variable was created.
Here is the expected command output.
Verify if the Powershell Constrained Mode was enabled.
Here is the expected command output.
In our example, we configured the Powershell Constrained Mode using a GPO.
