Would you like to learn how to do a Magento installation on Ubuntu Linux? In this tutorial, we are going to show you how to install, configure and access the Magento CMS on a computer running Ubuntu Linux.
• Ubuntu Linux Version 18.04
• Magento Version 2.3.0
Hardware List:
The following section presents the list of equipment used to create this Magento tutorial.
Every piece of hardware listed above can be found at Amazon website.
Magento Related Tutorial:
On this page, we offer quick access to a list of tutorials related to Magento.
Tutorial - NTP on Ubuntu Linux
First, we are going to configure the system to use the correct date and time using NTP.
On the Linux console, use the following commands to set the correct timezone.
# dpkg-reconfigure tzdata
Install the Ntpdate package and set the correct date and time immediately.
# apt-get update
# apt-get install ntpdate
# ntpdate pool.ntp.br
The Ntpdate command was used to set the correct date and time using the server: pool.ntp.br
Let's install the NTP service.
# apt-get install ntp
NTP is the service that will keep our server updated.
Use the command date to check the date and time configured on your Ubuntu Linux.
# date
If the system shown the correct date and time, this means that you followed all the steps correctly.
Tutorial - MySQL Installation on Ubuntu Linux
Now, we can proceed to the installation of the database service.
On the Linux console, use the following commands to install the required packages.
# apt-get update
# apt-get install mysql-server mysql-client
After finishing the installation, use the following command to access the MySQL database server.
# mysql -u root -p
Use the following SQL command to create a database named Magento.
CREATE DATABASE magento CHARACTER SET UTF8 COLLATE UTF8_BIN;
Use the following SQL command to create a database user named magento.
CREATE USER 'magento'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'kamisama123';
Give the sql user named magento permission over the database named magento.
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON magento.* TO 'magento'@'%';
quit;
Tutorial - Installing Apache on Linux
Now, we need to install the Apache web server and all the required software.
On the Linux console, use the following commands to install the required packages.
# apt-get install apache2 php7.2 php7.2-mysql libapache2-mod-php7.2 php7.2-cli
# apt-get install php7.2-mbstring php7.2-xml php7.2-zip php7.2-gd php7.2-xml
# apt-get install php7.2-bcmath php7.2-curl php7.2-intl php7.2-soap
Enable the Apache mod_rewrite and edit the apache2.conf file.
# a2enmod rewrite
# vi /etc/apache2/apache2.conf
Here is the original file, before our configuration.
DefaultRuntimeDir $
PidFile $
Timeout 300
KeepAlive On
MaxKeepAliveRequests 100
KeepAliveTimeout 5
User $
Group $
HostnameLookups Off
ErrorLog $/error.log
LogLevel warn
IncludeOptional mods-enabled/*.load
IncludeOptional mods-enabled/*.conf
Include ports.conf
Options FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride None
Require all denied
AllowOverride None
Require all granted
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride None
Require all granted
AccessFileName .htaccess
Require all denied
LogFormat "%v:%p %h %l %u %t "%r" %>s %O "%i" "%i"" vhost_combined
LogFormat "%h %l %u %t "%r" %>s %O "%i" "%i"" combined
LogFormat "%h %l %u %t "%r" %>s %O" common
LogFormat "%i -> %U" referer
LogFormat "%i" agent
IncludeOptional conf-enabled/*.conf
IncludeOptional sites-enabled/*.conf
At the end of the file, add the following lines.
<Directory /var/www/html>
AllowOverride All
</Directory>
Here is the new file with our configuration.
DefaultRuntimeDir $
PidFile $
Timeout 300
KeepAlive On
MaxKeepAliveRequests 100
KeepAliveTimeout 5
User $
Group $
HostnameLookups Off
ErrorLog $/error.log
LogLevel warn
IncludeOptional mods-enabled/*.load
IncludeOptional mods-enabled/*.conf
Include ports.conf
Options FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride None
Require all denied
AllowOverride None
Require all granted
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride None
Require all granted
AccessFileName .htaccess
Require all denied
LogFormat "%v:%p %h %l %u %t "%r" %>s %O "%i" "%i"" vhost_combined
LogFormat "%h %l %u %t "%r" %>s %O "%i" "%i"" combined
LogFormat "%h %l %u %t "%r" %>s %O" common
LogFormat "%i -> %U" referer
LogFormat "%i" agent
IncludeOptional conf-enabled/*.conf
IncludeOptional sites-enabled/*.conf
AllowOverride All
Now, you should find the location of the php.ini file on your system.
After finding, you need to edit the php.ini file.
# updatedb
# locate php.ini
# vi /etc/php/7.2/apache2/php.ini
Keep in mind that your PHP version and the location of the file may not be the same of mine.
Here is the original file, before our configuration.
file_uploads = On
max_execution_time = 30
memory_limit = 128M
post_max_size = 8M
max_input_time = 60
; max_input_vars = 1000
output_buffering = 4096
Here is the new file with our configuration.
file_uploads = On
max_execution_time = 300
memory_limit = 256M
post_max_size = 32M
max_input_time = 60
max_input_vars = 4440
output_buffering = off
You should also restart apache manually and verify the service status.
# service apache2 stop
# service apache2 start
# service apache2 status
Here is an example of the APache service status output.
● apache2.service - LSB: Apache2 web server
Loaded: loaded (/etc/init.d/apache2; bad; vendor preset: enabled)
Drop-In: /lib/systemd/system/apache2.service.d
└─apache2-systemd.conf
Active: active (running) since Mon 2018-04-23 00:02:09 -03; 1min 4s ago
Tutorial - Magento Installation on Ubuntu
First, let's install the Composer software.
Download and install the composer software using the following commands.
# mkdir /downloads/composer -p
# cd /downloads/composer
# php -r "copy('https://getcomposer.org/installer', 'composer-setup.php');"
# php composer-setup.php --install-dir=/usr/local/bin --filename=composer
Create a system user named Magento and make this user member of the Apache www-data group.
# useradd magento
# usermod -g www-data magento
Now, we need to install the Magento CMS on Ubuntu Linux.
On the Linux console, use the following commands to download the Magento package.
# cd /downloads
# wget -O magento2-2.3.0.tar.gz https://codeload.github.com/magento/magento2/tar.gz/2.3.0
# tar -zxvf magento2-2.3.0.tar.gz
Move all the Magento files to the root directory of your Apache installation.
Set the correct file permission on all moved files.
# mv /downloads/magento2-2.3.0 /var/www/html/magento
# cd /var/www/html/magento
# composer install
# find var vendor pub/static pub/media app/etc -type f -exec chmod g+w \;
# find var vendor pub/static pub/media app/etc -type d -exec chmod g+ws \;
# chown magento.www-data /var/www/html/magento -R
# chmod u+x /var/www/html/magento/bin/magento
Open your browser and enter the IP address your web server plus /magento.
In our example, the following URL was entered in the Browser:
• http://35.162.85.57/magento
The Magento web installation interface should be presented.

Click on the Start Readiness Check button and verify if all the requirements were met.
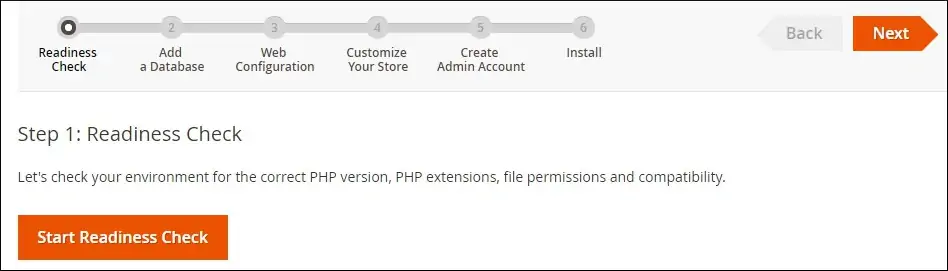
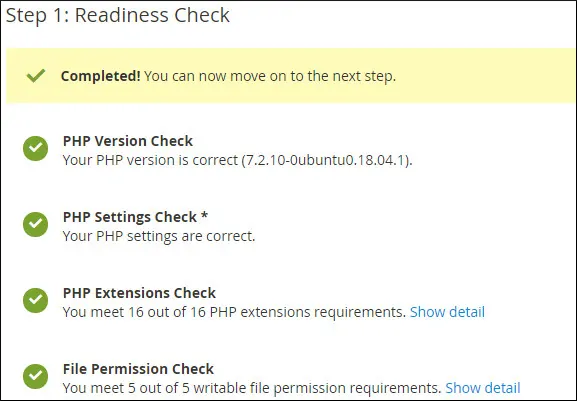
In our example, all requirements were met successfully.
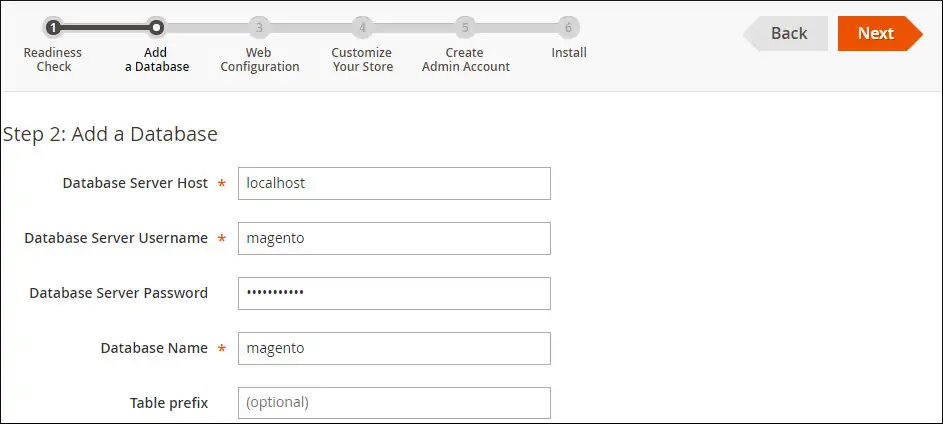
Enter the MySQL connection information to the Magento database.
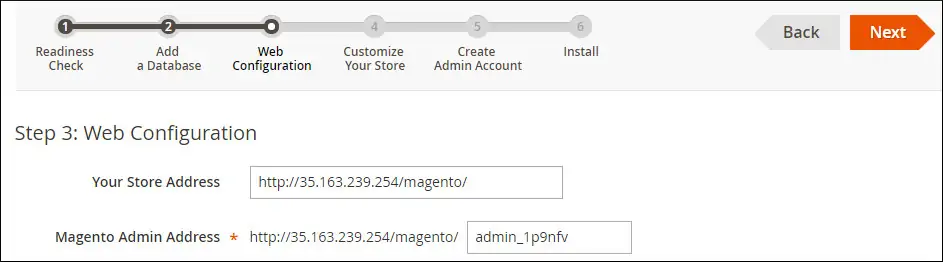
Enter your website URL and take note of your Administrative URL.
Select the desired language, currency and timezone.
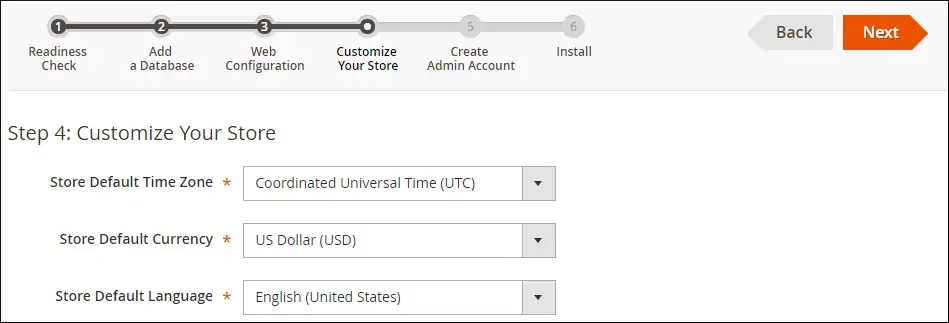
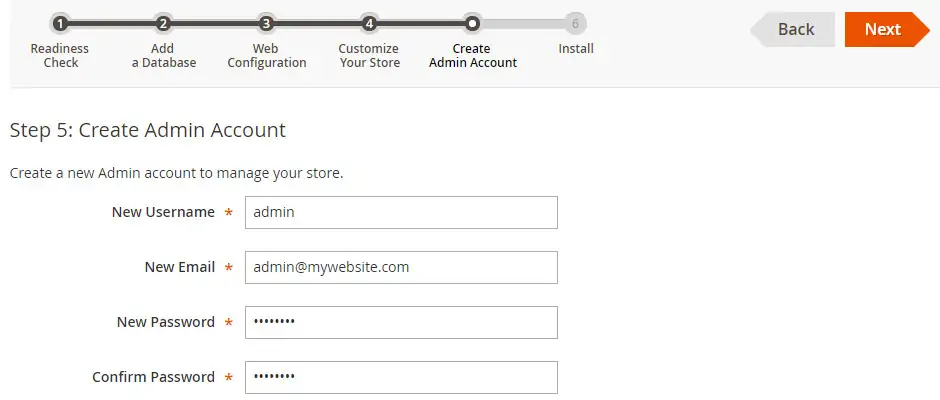
Enter the following administrative account information.
• Your administrator username.
• Your administrator e-mail account.
• Your administrator password.
Wait for the Magento installation to finish.
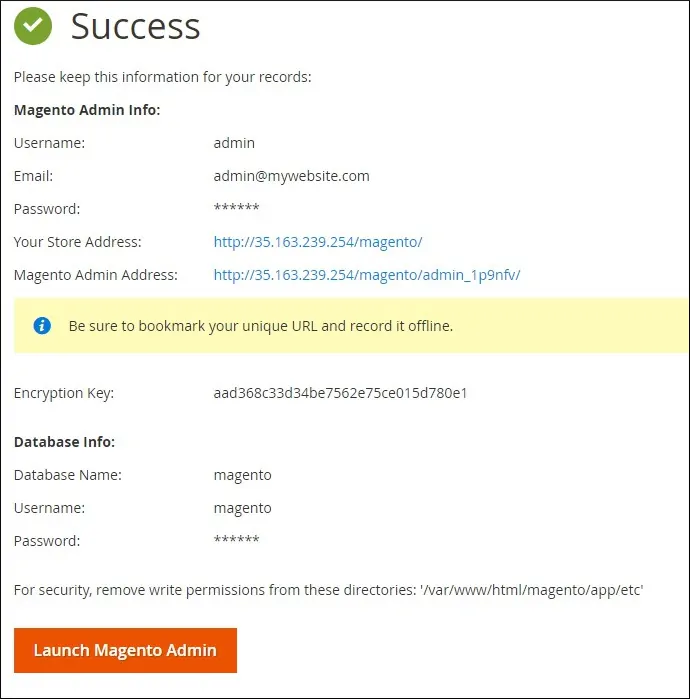
Take a look at your Magento installation summary.
Click on the Launch Magento Admin button.
After clicking on the button, you will be sent to the Magento login screen.

On the Magento Login screen, enter the Administrator username and Password.
After a successful login, you will be sent to the Magento Dashboard.
Congratulations, you successfully installed Magento on Ubuntu Linux.
After finishing the installation, you need to create a scheduled task on the Linux server.
On the Linux console, use the following command to create the required schedule task.
# cd /var/www/html/magento/bin/
# ./magento cron:install
Crontab has been generated and saved
