Would you like to learn how to configure file association on Windows using the command line? In this tutorial, we are going to show you how to associate a file extension to a specific program.
• Windows 2012 R2
• Windows 2016
• Windows 2019
• Windows 10
• Windows 7
Equipment list
The following section presents the list of equipment used to create this tutorial.
As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
Windows Related Tutorial:
On this page, we offer quick access to a list of tutorials related to Windows.
Tutorial Windows - Create a new file association using the command-line
As an Administrator, start an elevated command-line.
Associate a file extension with a file type.
Verify the file extension association.
Here is the command output:
In our example, we associated the file extension TC1 with the file type named TC1FILE.
Create a new file type.
Associate a command to open this file type.
Verify the command associated with the file type.
Here is the command output:
In our example, the file type named TC1FILE was associated with the notepad application.
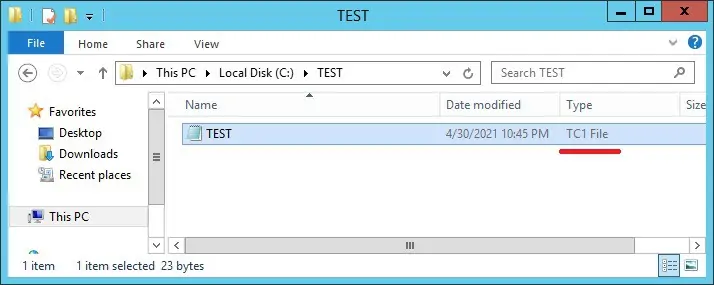
Create a file using the extension TC1.
Double-click the file with the new extension.
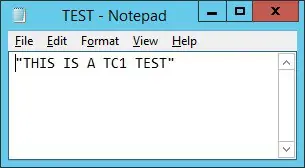
The Notepad application will automatically open the new file extension.
In our example, we associated a file extension with a file type.
In our example, we associated a file type with a command.
Congratulations! You are able to configure file association using the command-line on Windows.
Tutorial Windows - Configure a file association using the command-line
As an Administrator, start an elevated command-line.

Verify the file type associated with a file extension.
Here is the command output:
In our example, the TXT extension is associated with the file type named TXTFILE.
Configure this file type to be associated with another program.
Verify the command associated with the file type.
Here is the command output:
In our example, the file type named TXTFILE was associated with the WORDPAD application.
Congratulations! You are able to configure file association using the command-line on Windows.
